Full Chart:
https://igworks.com/blogs/growing-guides/nutrient-and-ph-chart-for-growing-hydroponic-fruits-and-vegetables?srsltid=AfmBOor_RXT-WKGGj7P25jQGXOZ-PKGrpEQ60MWKu2VKHq5IT_LTPNzG
Measurement Definitions & Full Chart
There are 5 “measurement terms” that you’ll likely encounter when researching how to grow your plants — pH, TDS, EC, cF, and PPM. Here’s what each one means:
Hydroponic Charts for Fruits and Vegetables: pH, TDS, EC, cF, PPM
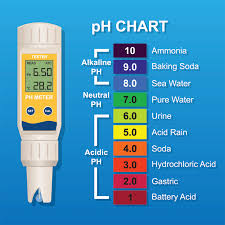
Nutrient solutions used for soilless culture should have a pH between 5 to 6 (usually 5.5), so the pH in the root environment is maintained between 6 to 6.5. This is the pH range at which nutrients are most readily available to plants.
In general, the ideal pH range for hydroponic crops is 5.5–6.0. However, different plants have different pH preferences, so it’s important to research the preferred pH range for the plants you’re growing.
pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is, with 7 being neutral. The pH of the nutrient solution affects how available nutrients are to the plants. If the pH is too low, it can prevent plants from accessing vital minerals. If the pH is too high, it can also prevent plants from accessing nutrients and can clog the hydroponic system.
To ensure your plants are getting the nutrients they need, it’s important to measure the pH regularly and maintain it within the optimal range. You can also use separate nutrient reservoirs for plants with similar pH ranges.